
But for small to middle size organizations, one ledger account is more than enough to record all their payables related to their employees. Debts are usually placed on the liability side of the balance sheet. Long-term liabilities are paid with fixed assets like equipment, non-liquid assets, equity, investment, etc. A security deposit paid by a tenant is generally considered an asset because it is an amount expected to be returned at the end of the lease, assuming the tenant fulfills their lease obligations.

Capital Expenditures vs Regular Expenses

If you’re still manually tracking your balance sheets, it might be time to explore accounting automation software. An accounting platform can help simplify and streamline the workflow via automation, saving you both time and money throughout the process. Insurance expense and insurance payable are two different things, yet they are interrelated. There would be no need for an insurance payable account if there were no insurance expense. There are three different accounting scenarios involving sales taxes, and the accounting treatment varies in each scenario.
Types of liabilities

For instance, if a tenant pays rent on December 28th for January’s occupancy, a cash basis tenant records it as an expense in December, and a cash basis landlord records it as revenue in December. Like revenue accounts, expense accounts are temporary accounts that income statement collect data for one accounting period and are reset to zero at the beginning of the next accounting period. A company’s assets are also grouped according to their life span and liquidity – the speed at which they can be converted into cash. Assets are broken out into current assets (those likely to be converted into cash within one year) and non-current assets (those that will provide economic benefits for one year or more). AP typically carries the largest balances because they encompass day-to-day operations.
How Liabilities Work
However, when the invoice is paid, it becomes a cash outflow, reducing the company’s available funds. Properly classifying liabilities and expenses is key to assessing your company’s short- and long-term financial health. They’re also essential to understanding its performance and ensuring accurate financial analysis. Liabilities are listed on the balance sheet and represent what the business owes. They help business owners understand the company’s ability to meet financial obligations and how much it relies on outside financing. Capital expenditures (CapEx) are investments in long-term assets like property or equipment, while regular expenses are short-term operational costs.
- Examples of non-current liabilities include long-term bank loans, bonds payable issued to investors, and lease obligations.
- The employer is keeping a record of the amount of money owed to the employee until it can be paid out.
- The term “account” is used often in this tutorial so let’s understand what it is before we proceed.
- Income accounts are temporary or nominal accounts because their balance is reset to zero at the beginner of each new accounting period, usually a fiscal year.
- It covers guarantees of debts, liquidated damages, government probes, and lawsuits.
- Each subsequent month, a portion of this prepaid amount is moved from the asset account to an insurance expense account on the income statement, reflecting the consumption of the coverage.
Tracking expenses can help with budgeting and tax deductions and provide an overview of your finances. Being able to distinguish between the two can improve your financial planning and performance for the future. Here, we provide clear definitions of expenses and liabilities in accounting, along with practical examples and guidance on how to classify and record each. The good news for companies about such types of insurance is that they can be deducted from tax liability as a business expense. However, most companies can deduct such expenses on their income tax forms in order to get a tax break.
Recording Accrued Expenses
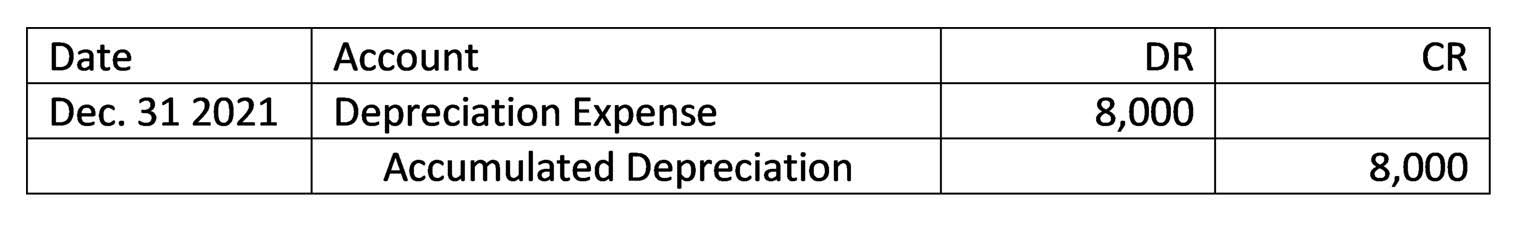
Current liabilities are expected to be paid back within one year, and long-term liabilities are expected to be paid back in over one year. It’s important for companies to keep track of all liabilities, even the short-term ones, so they can accurately determine how to pay them back. On a balance sheet, these two categories are https://autorenkanzlei-beckmann.de/small-business-bookkeeping-services-in-dallas/ listed separately but added together under “total liabilities” at the bottom. The difference between the salary expense and salary payable is the same that lies between an expense account and a liability account.
Capital
- Did it create an obligation, meaning a future cost that the company will owe?
- Liabilities and expenses play key role’s as part of your small business’s payroll accounting system.
- It flows into the statement of retained earnings, and the ending balance of retained earnings is then reported within the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet.
- So, employees who worked all of November will be paid in December.
- These represent obligations to third parties, such as tax authorities, benefits providers, or creditors, and remain until payment is made.
- However, the company’s accrued salary expenses are the expenses that the company is expected to incur based on its best estimate.
- Similarly, long-term loans represent borrowed funds that need to be repaid over an extended period.
The expense was posted in March when the restaurant employees worked the hours. Revenue in March is matched with March expenses, including the $3,000 in payroll costs. The accrual method posts payroll liabilities and expenses in the same period.
In financial discussions, the terms ‘expense’ and ‘liability’ are frequently used. While related, they represent different aspects of a company’s financial activities and are not interchangeable. Understanding their distinct roles is a foundational part of grasping a company’s financial health, as their proper classification is required for accurate financial reporting. Liabilities often appear on the balance sheet, affecting the company’s assets and equity, while expenses appear on the income statement, directly impacting net income. An expense refers to the costs incurred by an individual, business, or organization in order to generate revenue or achieve specific objectives. It is the outflow of resources, in the form of money, to pay for goods, services, or obligations.
Understanding Financial Classifications
At each period-end, companies reset this account to cover one period only. Usually, companies use this account to create an expense during a financial period. This site records the different accounts impacted by is a liability an expense the wages expenses. It is a part of a double-entry to record an increase in the wages incurred during a period.
